endometrium
Endometrium
The endometrium is a mucosa of uterus which is continuously remodeled during the menstrual cycle. Its primary function is to create the optimum environment for implantation of the blastocyst after fertilization. It is sensitive to hormones (estrogen and progesterone). Before puberty the correct thickness is from 0.3 to 0.5 mm. It is important that the uterus does not have a submucosa tissue - muscle membrane connects to the mucous membrane directly.
Structure
a) monolayer cylindrical epithelium (also includes uterine glands);
b) stroma (or lamina properthat includes connective tissue and vessels).
Division of the stromal layer
a) functional (dense, spongy - peels off in the final luteal phase);
b) basal (regenerating - a building block to reproduce functional layer).
The variability of the endometrium according to menstrual cycle phase - during the follicular phase, estrogen concentration constantly increases, which stimulates the development of ducts glands, accumulation of glycogen and angiogenesis (the formation of spiral arteries). Endometrium is thickening, epithelium and glands are recreated. At the end, of the follicular phase corpus luteum secretes progesterone (the entrance to the luteal phase). Glands are still expanding and extending, also receive a rich vascularization from the spiral arteries. During this phase, stromal cells receive more glycogen, enzymes, lipids.
There is a variety of layers (compacted - decidual cells of the epithelium, spongy - ductus glands). After fertilization, progesterone concentration increases - it prepares the endometrium for implantation of the embryo. When there is no fertilization, corpus luteum dies and progesterone concentration decreases. It makes sudden ischemia, and later vasodilatation, which burst and pour blood on the outside. This leads to scaling of functional layer of the mucosa (menstrual period).
Pathology
The endometrium affects many types of diseases, the most popular are:
a) cancer of the uterus (closely associated with hormonal balance),
b) hyperplasia of the endometrium (endometrial hyperplasia with atypia or without atypia);
c) endometriosis (the presence of endometrial lesions outside the uterine cavity).
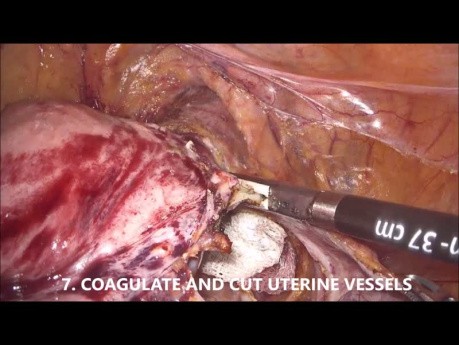
Goel's Technique of Laparoscopic Hysterectomy...
Demonstrating the Goels technique of hysterectomy for carcinoma endometrium. This innovative method is instrumental in minimizing complications in carcinoma endometrium surgeries, leading to better patient...
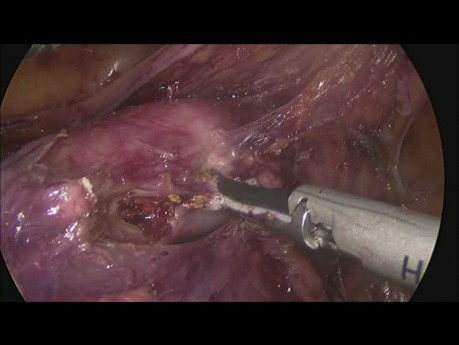
Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy + Lymphadenectomy...
Surgical video case: for performing a hysterectomy one can use many energy devices. It's difficult to complete the entire procedure with a single energy device. To perform a laparoscopic hysterectomy,...
Rudimentary Horn/ Endometriosis / Chocolate Cyst
A case of left rudimentary non communicating horn with active endometrium lead to hematosalpinx with perforation and chocolate peritonitis.
Hysteroscopic Resection Senile Polyp
Post menopausal senile polyp was diagnosed. Patient was asymptomatic. Patient also had 1 degree prolapse with cystocele for which she was not symptomatic. Bipolar 22fr resectoscope is used to resect the...
Hysteroscopic Polypectomy
Adenomatous polyp in endometrium are better removed by hysteroscopic method.
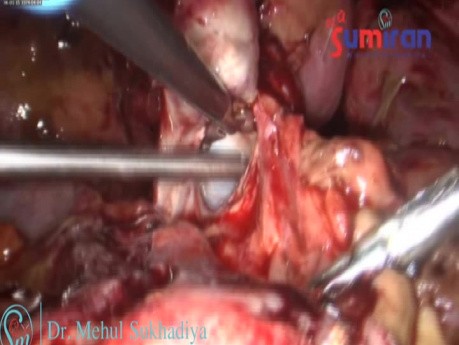
TLH + BSO
Sure you have done many, so I leave a hysterectomy of "daily", as it could leave yesterday or tomorrow... a complex hyperplasia with atypia in postmenopausal woman, hence the tubal seal. I have...
8.6 x 7 cm Fundal Wall Highly Vascular Fibroid...
DIGNOSIS:-8.6 x 7 cm Fundal Wall highly vascular fibroid With Disturbing Cavity. TREATMENT (PLAN OF SURGERY): - lap.myomectomy + hystroscopy DLS done under general anaesthesia given by dr amit and...
3 x 3 cm Adenomatous Cyst Disturbing Cavity
DIGNOSIS :- 3 x 3 cm Adenomatous cyst Disturbing Cavity. TREATMENT (PLAN OF SURGERY) :- DLHS DLHS done under general anaesthesia given by dr Chirag Barochiya and done by dr pravin kanani. LAPROSCOPY:...
Endometrial cancer
A 47-year-old woman with diagnosed G3 endometrial cancer. In MR imaging, infiltration of over half of the musculature. The film shows, in particular, the technique of removing the aortic nodes without...