cataract
Cataract
Cataract. is a disease of the lens, which is characterized by the presence of opacities within the structure of the eye and ultimately leads to blindness. It is one of the most common causes of vision loss in people over 60 years of age.
Symptoms in adults
In the development of the disease comes to a gradual deterioration of visual acuity, haze appear on a picture (depending on the type of cataract), disturbances in the evaluation of the distance, difficulty in performing daily activities in older adults. There is one or both eyes.
Symptoms in children
Are a bit different than for adults. The most characteristic is the white color of the pupil (leukokoria), in the later stages of the disease may occur strabismus and nystagmus.
Types
The current classifications divide cataracts due to:
a) origin - differentiate acquired and congenital cataract (child), the former is characterized by a gradation of severity of changes - from the initial cataract (clouding occurs at the periphery of the lens) through advanced (haze covers the entire lens, resulting in visual impairment), immature (for blindness), mature (half the total haze), swelling (water absorption and swelling), to liquidate the lens fibers - can lead to inflammation of the tissues inside the eye and irreversible blindness, cataracts shares acquired due to the location of the lesions (cataract layered, nuclear, total, capsularis front, rear capsularis, polar, membranous) and is already present at birth.
b) cause:
- senile cataract (age-related development)
- cataract followed: diabetic, tetany, cortisone (after application of
glucocorticoids), galactose
- traumatic cataract (after injuries, blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, exposure to radiation, work in the mill, the operation of electricity)
- cataract complicated (secondary) - occurs as a complication of other eye diseases (e.g. glaucoma).
Treatment
In the case of congenital cataract should be taken as soon as possible. The only effective cure for this disease is surgical removal of the opaque lens with subsequent placement of a new lens (without the lens does not allow for comfortable vision - there is no accommodation, and remains high hyperopia). The most common method is phacoemulsification (fragmentation and removal of old lenses without disturbing the posterior capsule, intraocular lens implantation). It is also possible to remove the opaque structure without shredding. Instead of implanting intraocular lens, you can also use special contact lenses.
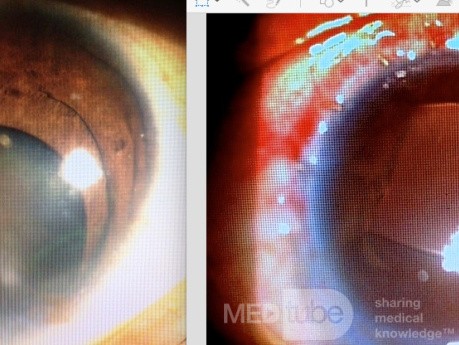
Microcornea Plus Black Cataract
Pt with a very small cornea with black cataract came for IOL implantation. I/C surgery was done and iris claw lens implanted at the back of the cornea. Incision was sealed with steel sutures.
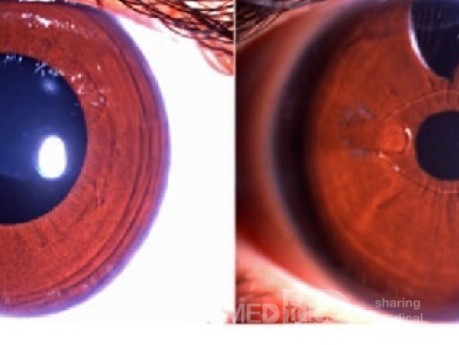
Lens Implantation in Megalocornea
Subluxated cataract removed by dry aspiration and a small sized iris claw lens fixed to the front.