furuncle
Furuncle
Furuncle (boil) is a change caused by purulent inflammation of the hair follicle and its area. Causative factors are usually streptococci or staphylococci.
Typical location : face, back, neck, chest and buttocks. Furuncle may be larger than 3 cm diameter. At the top there is a point (near hair) , and inside is created thrombus necrosis. Described process is accompanied by large pain and redness. After a while, furuncle emptied with pus spontaneously and inflammation disappears. Change heals by granulation and leaves a scar. The average recovery time is between 10 and 25 days. In patients who are predisposed (congenital and secondary immunodeficiency, diabetes mellitus), infection can be more serious.
Signs that could suggest the appearance of boil are: itching, mild swelling and pain.
Types
a) Furunculosis (Job syndrome) - a term used in the presence of multiple boils, it is common in people with decreased immune systems.
b) Carbuncle (plural boils) - concentration of several furuncles which are joined. It appears most frequently in the neck area (the most common place for abrasion), rarely on other hairy parts of the body (thighs, genitals, buttocks).
c) Boil around the triangle of death – topographically the triangle of death is an area on the face where vertices are determinated by lip corners and top of the nasal pyramid. Venous flow is important in this area - drainage vessels have a finish in the cavernous sinus (inside the cranial cavity). This creates a high risk of infection’s spreading and consequently it creates cavernous sinus thrombosis. The conclusion is simple - you should not squeeze this area.
d) Boil of the nasal vestibule - a special kind of facial furuncle which may be associated with various complications. The characteristic symptoms are: tenderness in the nostrils, swelling in the nasal vestibule, upper lip and wings. The disease may be complicated by the following problems: facial phlegmon or eye socket, nasal abscess, facial thrombophlebitis or eye socket, meningitis, sepsis. Antibiotic therapy ( intravenously)is very important.
Treatment
Local antibiotic therapy; in the case of facial boils and furunculosis - systemic antibiotic therapy (intravenous); in resistant cases - surgical intervention (contraindicated in case of boils in the triangle of death).
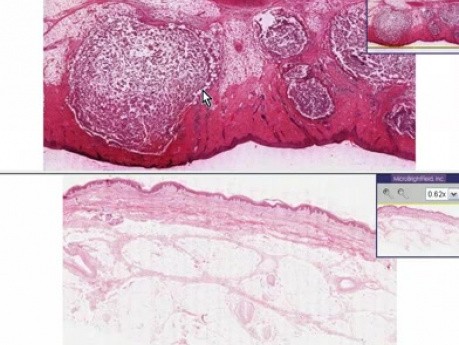
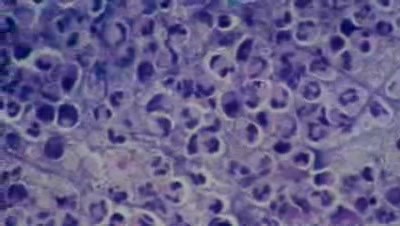
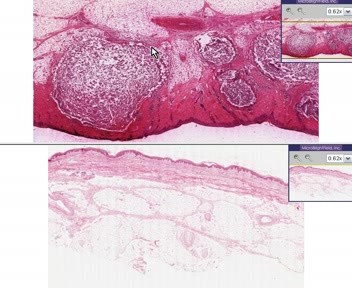
Furuncle (abscess) - Histopathology - Skin
This video shows furuncle in histopathological image of abscess.
Furuncle (Abscess)
What is the definition of a furuncle? Is it different from a carbuncle? Are these abscesses primarily involving the dermis or epidermis? Delineate some dermal abscesses.