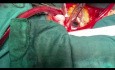
Psoic Bladder with Ureteral Reimplantation
Case description
Abstract: we present a case of ureteral stenosis below the crossing of the iliac vessels after surgery to treat endometriosis.
Initially, the patient had a ureteral fistula / urinoma and later the presence of stenosis.
We demonstrate a technique for passing a guidewire and a double-J catheter using a Veress needle as an aid.
Ureteral reimplantation with psoic bladder through robotic-assisted laparoscopy using the Versius platform.
Psoic bladder with ureteral reimplantation:
Female patient, 56 years old, after gynecological surgery – laparoscopic hysterectomy for endometriosis. Evolves with pain in the lower abdomen. Follow-up exams soon after surgery showed no noteworthy alterations.
After the pain persisted for more than 6 months, she looked for another gynecologist, who requested a new ultrasound to screen for endometriosis, which indicated alterations suggestive of recurrence in the right ovary.
She underwent laparoscopic oophorectomy. On the seventh postoperative day, she had diffuse abdominal pain, with fever and altered intestinal transit. Imaging – contrast-enhanced abdominal computed tomography – shows a right distal ureteral fistula at the level of the crossing of the iliac vessels with moderately intense dilation.
Requested urological evaluation, which initially indicates local control with double J catheter. Submitted to cystoscopy for catheter insertion, with no guidewire progression. At the same time, ureteroscopy was performed, which showed stenosis of the distal ureter, with damage to the upstream ureteral mucosa (distance between the stenosis and a fistula was approximately 2 cm). After passage of double J 6Fr, passage remains asymptomatic. This stays for 28 days. Control tomographic examination does not show fistula, with reduction of dilation of the ureteral/pelvic system, which was removed.
40 days after the removal of the double J, an asymptomatic patient, a new exam was indicated, who underwent a contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging, which showed a new dilation of the high collecting system, with signs of ureteral stenosis in the same segment identified in ureteroscopy, with delayed emission of the contrast.
At this time, ureter reimplantation was indicated, and the robotic-assisted laparoscopic technique was chosen.
This surgery was didactically divided into 14 stages:
1- Right ureter identification – 4s.04
2- Release of plans and identification of iliac vessels – 12s.29
3- Ureter release and vessel loop passage – 1min.40s.03
4- Dissection of fibrotic tissue, with an attempt to “gain” the maximum amount of healthy ureter – 3min
5- Bladder release – 4min.29s.54
6- Psoic bladder – 5min.37s.38
7- Site marking for future anastomosis – 7min.17s.28
8- Muscular opening, preserving the bladder mucosa – 7min.26s.54
9- Fixation of the ureter in two points (6 and 12h) – 7min.40s.21
10- Opening of the vesical mucosa – 8min.7s.23
11- Medial plane suture – 8min.23s.03
12- Passage of a guidewire and double-J through the lateral face using a Veress needle – 8min.46s.01
13- Lateral face suture – 10min.09s.92
14- Cystoscopic control – correct position of the double j catheter, without leakage through the anastomosis – 10min.43s.86 The patient remains hospitalized for two days. Blake drain with a maximum of 50 ml every 24 hours, being removed at discharge.The indwelling urinary catheter, in turn, was removed on the 4th postoperative day.Double J catheter removed on the 24th postoperative day.
Robotic Ureteral Reimplantation.
Passoni N, Peters CA. J Endourol. 2020 May;34(S1): S31-S34. doi: 10.1089/end.2019.0619. Epub 2020 Mar 24. PMID: 32207993
Robot-assisted laparoscopic ureteral reimplantation in children: a valuable alternative to open surgery.
Gerber JA, Koh CJ. World J Urol. 2020 Aug;38(8):1849-1854. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02766-y. Epub 2019 Apr 19. PMID: 31004205
Robotic Ureteral Reconstruction.
Drain A, Jun MS, Zhao LC. Urol Clin North Am. 2021 Feb;48(1):91-101. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2020.09.001. Epub 2020 Nov 5. PMID: 33218597
Ureteral Reimplantation, Psoas Hitch, and Boari Flap.
White C, Stifelman M. J Endourol. 2020 May;34(S1):S25-S30. doi: 10.1089/end.2018.0750. PMID: 32459151
Ureteral reimplantation in adults: open versus robotic.
McClung C, Gorbonos A. J Urol. 2014 Oct;192(4):1023-5. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.07.020. Epub 2014 Jul 16. PMID: 25038466
Robotic assisted ureteral reimplantation: current status.
Stanasel I, Atala A, Hemal A. Curr Urol Rep. 2013 Feb;14(1):32-6. doi: 10.1007/s11934-012-0298-1. PMID: 23263873