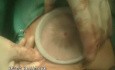
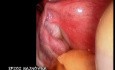
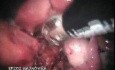
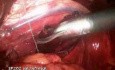
Endoscopic Islets Autotransplantation
Case description
1. Department of General and Transplantation Surgery, Warsaw Medical University, Warsaw, Poland
2. Department of Transplantology and General Surgery, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Bydgoszcz, Poland
3. Department of Immunology, Transplantology and Internal Diseases, Warsaw Medical University, Warsaw, Poland
4. Department of Internal Diseases and Cardiology, Warsaw Medical University, Warsaw, Poland
5. Department of Nephrology and Transplantology, Warsaw Medical University, Warsaw, Poland
6. First Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care, Warsaw Medical University, Warsaw, Poland
7. Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Maria Sklodowska-Curie Memorial Cancer Center and Institute of Oncology, Warsaw, Poland
8. Department of Clinical Radiology, Warsaw Medical University, Warsaw, Poland
♯Corresponding author: Michal Wszola MD, PhD, Department of General and Transplantation Surgery, Warsaw Medical University, 59 Nowogrodzka Street, 02-006 Warsaw, Poland. Tel:+48225021470,Fax:+48225022155 e-mail: [email protected]
Abstract
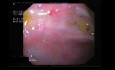
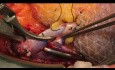
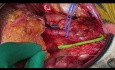
Chronic pancreatitis (CP) is a severe illness, which may cause significant deterioration of patients’ quality of life because of constant pain. Pancreatic resection followed by pancreatic islets autotransplantation might be a successful therapeutic option for a selected group of patients. Successful islets transplantation into gastric sub-mucosa in a pre-clinical study on pigs makes gastric submucosa a promising option for future. Aim of this paper was to report a successful resection of the pancreas and endoscopic islets autotransplantation into gastric sub-mucosa in man. Patient and methods. A 53-year old man with alcohol- related chronic pancreatitis for 15 years was operated on. Patient underwent pancreatectomy. Endoscopic gastric sub-mucosa transplantation was performed 6 hours later. Levels of fasting c-peptide were measured prior to the procedure and at 1,2,3,4,5,7,14, 30, 90 and 180 days post autotransplantation. C-peptide stimulation (CPS) test was performed prior to the procedure and one, three and six months post autotransplantation. Fasting glycemia and oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) was performed prior and at 7, 30, 90 and 180 days post transplantation. Control gastroscopy and endoultrasonography (EUS) were performed within first week post-transplantation. Results: Isolation: 264 000 IEQ were isolated. Pellets had 6 ml and were suspended in 60 ml of Ringer’s solution. Patient did not require any insulin or oral hypoglycemics post surgery. Pre-procedure fasting c-peptide was 0.89 ng/ml. Post-procedure C-peptide was between 0.44 and 1.36 ng/ml. Conclusion. Preliminary results of endoscopic gastric sub-mucosa islets autotransplantation indicate that it might be an alternative site for islets autotransplantation in case of patients with contraindication for transplantation into the portal vein.
This user also sharing
Laparoscopic Right Hemicolectomy
Michał Wszoła
views: 14171
Diagnostic Laparoscopy
Michał Wszoła
views: 9076
Hiatal Hernia
Michał Wszoła
views: 5257
Recommended
Mini Incision Kidney Transplantation
Serkan Akinci
views: 1348
The Diagnosis of Brain Death
views: 2757